Simple Manometers
A simple manometer is one which consists of a glass tube, whose one end is connected to a point where pressure is to be measured and the other end is open to atmosphere.
Piezometer
Piezometer is one of the simplest forms of manometers. It can be used for measuring moderate pressures of liquids. The setup of piezometer consists of a glass tube, inserted in the wall of a vessel or of a pipe. The tube extends vertically upward to such a height that liquid can freely rise in it without overflowing. The pressure at any point in the liquid is indicated by the height of the liquid in the tube above that point.
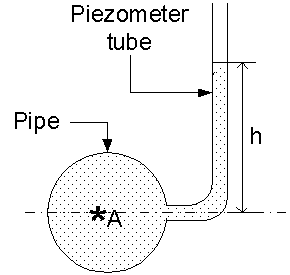
Pressure at point A can be computed by measuring the height to which the liquid rises in the glass tube. The pressure at point A is given by p = wh, where w is the specific weight of the liquid
Limitations of Piezometer
1. Piezometers can measure gauge pressures only. It is not suitable for measuring negative pressures.
2. Piezometers cannot be employed when large pressures in the lighter liquids are to be measured since this would require very long tubes, which cannot be handled conveniently.
3. Gas pressures cannot be measured with piezometers, because a gas forms no free surface.
A simple manometer is one which consists of a glass tube, whose one end is connected to a point where pressure is to be measured and the other end is open to atmosphere.
Piezometer
Piezometer is one of the simplest forms of manometers. It can be used for measuring moderate pressures of liquids. The setup of piezometer consists of a glass tube, inserted in the wall of a vessel or of a pipe. The tube extends vertically upward to such a height that liquid can freely rise in it without overflowing. The pressure at any point in the liquid is indicated by the height of the liquid in the tube above that point.

Pressure at point A can be computed by measuring the height to which the liquid rises in the glass tube. The pressure at point A is given by p = wh, where w is the specific weight of the liquid
Limitations of Piezometer
1. Piezometers can measure gauge pressures only. It is not suitable for measuring negative pressures.
2. Piezometers cannot be employed when large pressures in the lighter liquids are to be measured since this would require very long tubes, which cannot be handled conveniently.
3. Gas pressures cannot be measured with piezometers, because a gas forms no free surface.